The way catalysts are used vary widely, Some examples include polymer production and different types of reactors for solid homogeneous catalysts..
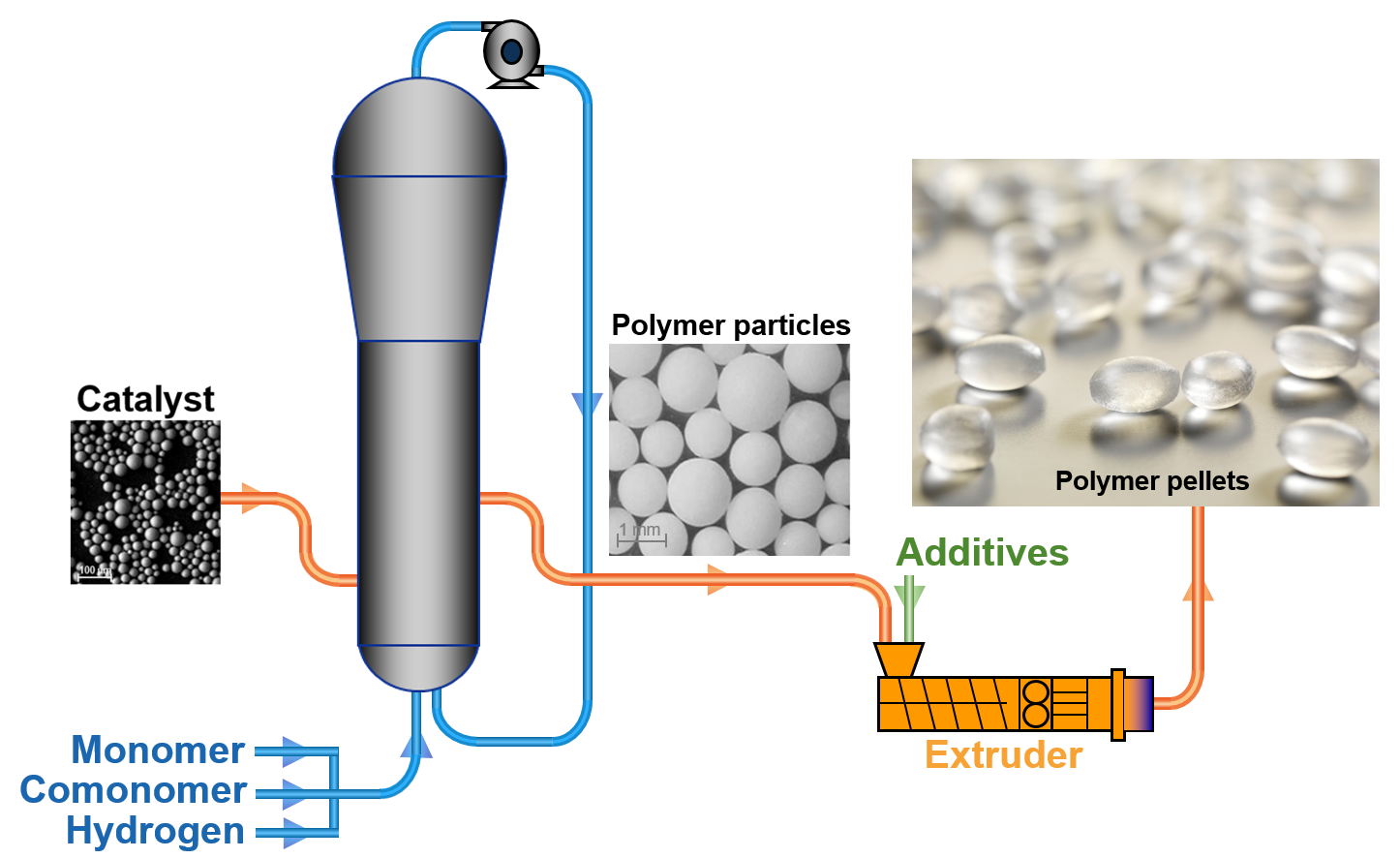
An example of the manufacture of polymers where the catalyst is injected in a reactor containing the monomer and hydrogen under pressure where the polymer particles are formed and removed from the reactor.
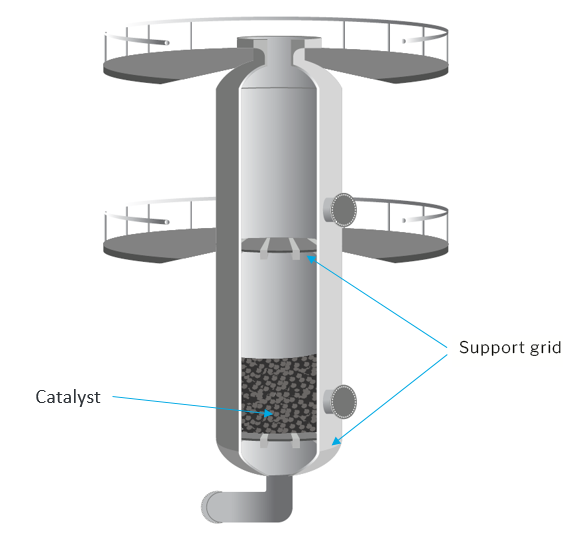
A fixed bed reactor is the most common type and is typically a cylindrical vessel filled with catalyst pellets with the gas or liquid reactants flowing down-flow through the bed and being converted into products
The reactor may have multiple configurations including one large bed or several beds in series.
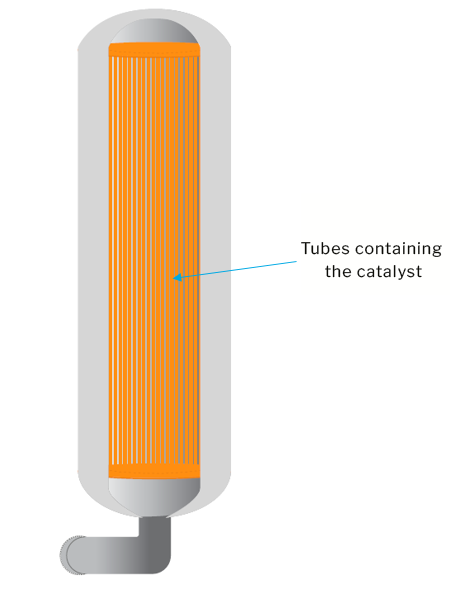
This consists of a series of tubes containing the catalyst
This is normally used where the process has to be carried out at high temperature where hot gases are on the outside of the tubes. Tubular reactors are also used where the process is highly exothermic and coolant is on the outside of the tube and where it is difficult to obtain and maintain the temperatures if a single bed was utilized.
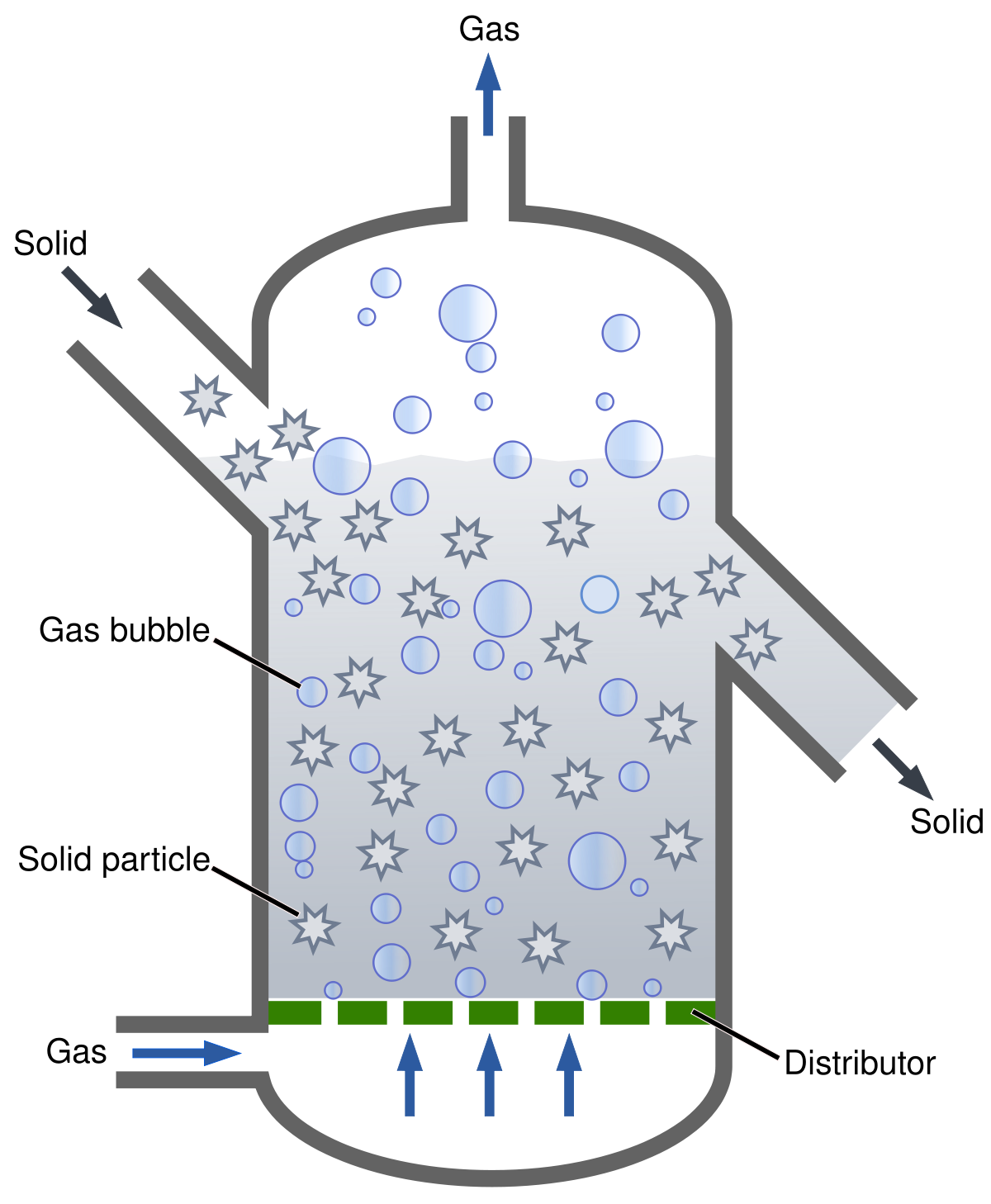
A fluidised bed reactor suspends small catalyst particles by the upward motion of the fluid to be reacted. The fluid is typically a gas with a flow rate high enough to mix the particles without carrying them out of the reactor
Fluidised bed reactors are typically multiple vessel units whereby under normal operation, the catalyst will migrate between vessels. This allows the catalyst to be moved through the vessel and into regeneration sections that will regenerate the catalyst and return it to the top of the reactor. A common fluid bed reactor is for Fluid Catalytic Cracking (FCC) used to crack heavy hydrocarbon feedstocks.


